Menopause Treatment
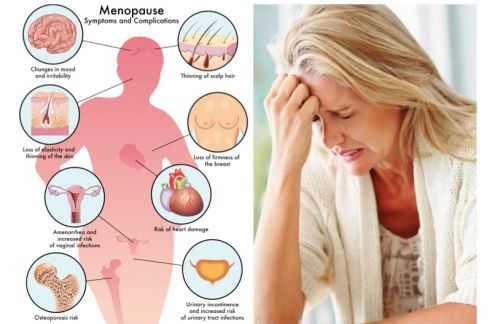
Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s menstrual cycles and fertility. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, though it can vary from woman to woman. Menopause is officially diagnosed when a woman has gone 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period.
This phase represents a significant transition in a woman’s life, driven by a gradual decline in the production of reproductive hormones, primarily estrogen and progesterone, by the ovaries. While menopause is not a disease or disorder, it can bring about a variety of physical and emotional changes due to hormonal fluctuations.